Usage
When to use
- To trigger an action or event, like a form submission.
- For links that require more prominence, such as CTAs (calls-to-action), see Links as Buttons.
- For links that are part of an inverse button group, see Links as Buttons.
When not to use
- For links that are not CTAs or part of an inverse button group, consider Inline or Standalone link.
- To display multiple actions under a single button, use Dropdown.
Sizes
Medium is the preferred size, but use a Button size that best fits the UI (e.g., don’t use a large button in a table).
Full-width buttons fill 100% of the parent container. Use full-width Buttons sparingly.
Types
Primary
Use Primary for the most important action on a page, e.g., for submitting a form. Avoid using multiple Primary buttons on a single page.
Secondary
Use Secondary for less important actions or when multiple actions of the same importance are needed.
For example:
- for
Cancelnext to aSubmitbutton. - when needing to let the user do things like
DownloadorGeneratea report but neither are the primary focus or goal of the page.
Critical
Use Critical when users take an action that is potentially dangerous. For example, when deleting a cluster.
Tertiary
Use Tertiary for low-priority actions when lighter visual weight is required.
For example:
- for actions on a page that require even less visual weight or priority than a secondary button (our default for less important actions).
- for controlling form fields (such as adding an additional form field).
Icon position
Buttons are provided with flexible icon use; allowing for leading, trailing, or icon only buttons. Use icons intentionally and only when they provide the user with extra value. Do not create buttons with both leading and trailing icons. Tertiary buttons are required to have either a leading or trailing icon layout to be accessible.
Leading
In most cases, use leading icons. Choose icons that add meaning and clarity to the action described in the button’s text.
Use the leading position when creating or adding a new object.
Trailing
Consider trailing icons when guiding the user forward through the product.
Use chevron-right to indicate moving forward in a multi-step flow.
Use arrow-right when using the Button for internal links. In most cases, consider using a Standalone Link instead. For more details, please refer to the code documentation.
Use external-link when using the Button for external links. In most cases, consider using a Standalone Link instead. For more details, please refer to the code documentation.
Links as Buttons
The Button component accepts an @href or @route argument, which results in a link with the visual appearance of a button. While in general, we advise against this approach because it can cause confusion for keyboard-only users, there are a few instances where this may be appropriate for improved visual hierarchy, such as:
For links that require more prominence and CTAs (calls-to-action).
For links that are part of an inverse button group.
Learn more about how semantic use helps make our products more conformant.
Button set
ButtonSet is a layout component that provides consistent spacing between multiple Buttons. Refer to the ButtonSet documentation to learn more. ButtonSet is only available in code.
More detailed examples and guidance on button organization can be found in the button organization pattern documentation.
Content
- Text should be short and to the point (~25 characters). Buttons should not consist of full sentences, but should provide enough context to be useful.
- Language should be used consistently within each product (e.g., when using "Edit" on one page, use that same convention throughout the rest of the application, not "Change").
How to use this component
The basic invocation requires text to be passed:
<Hds::Button @text="Basic button" />
Add an icon
To add an icon to your Button, give the @icon any icon name:
<Hds::Button @text="Create cluster" @icon="plus" />
Icon position
By default, if you define an icon, it is placed in the leading position (before the text). If you need to position the icon in the trailing position (after the text), define @iconPosition:
<Hds::Button @text="Next step" @icon="arrow-right" @iconPosition="trailing" />
Icon-only Button
If you would like to create an icon-only Button, set @isIconOnly to true. Note that you still have to define the @text value; it will be used as the aria-label attribute value on the Button element.
<Hds::Button @text="Create cluster" @icon="plus" @isIconOnly= />
Color
There are four available colors for the Button: primary, secondary, tertiary, and critical. The default is primary. To use a different color, declare another value for @color:
<Hds::Button @text="Secondary" @color="secondary" />
<Hds::Button @text="Tertiary" @color="tertiary" @icon="bulb" />
<Hds::Button @text="Critical" @color="critical" />
Size
There are three sizes available for the Button: small, medium, and large. The default is medium. To use a different size, declare a value for @size:
<Hds::Button @text="Small button" @size="small" />
<Hds::Button @text="Large button" @size="large" />
Full-width
This indicates that the Button should take up the full-width of the parent container. It’s set to false by default.
<Hds::Button @text="Full width button" @isFullWidth= />
Layout
To change the default block layout to inline, set @isInline to true. This can be useful in contexts where the Button needs to be inline, for example to inherit the alignment from a parent.
<div class="doc-button-mock-text-align-right">
<Hds::Button @text="inline layout" @isInline= />
</div>
Type
This is the native HTML button attribute, type. There are three possible values: button, submit, and reset. The default type for the Button is button. To submit form data to the server, set type to submit.
<Hds::Button @text="Submit" type="submit" />
Actions
Define the action in your route or controller, and add it to the component invocation in your template:
Read the Ember.js guides for more information: Patterns for Actions .
<Hds::Button @text="Alert me" />
Links
You can generate a link with the visual appearance of a button, by passing an @href or a @route argument to the component.
If you’re passing an @href or a @route argument to the component, this will generate an <a> link, not a <button>. In this case, no type is needed.
With @href
If you pass an @href argument, an <a> link will be generated.
target=“_blank” and rel=“noopener noreferrer” attributes are applied by default. This is the most common case, as internal links are generally handled using a @route argument but can be overridden. If the href points to an internal link, or uses a different protocol (e.g., "mailto" of "ftp"), pass @isHrefExternal=false and it will not add the target and rel attributes.
<Hds::Button @text="Visit website" @icon="external-link" @iconPosition="trailing" @href="https://hashicorp.com" />
With @route
If you pass a @route argument, an <a> link will be generated using a <LinkTo> Ember component. All of the standard arguments for the <LinkTo/LinkToExternal> components are supported (eg. models/model/query/current-when/replace).
If the route is external to your current engine, you have to pass @isRouteExternal=true so it will use <LinkToExternal> instead of <LinkTo> for the @route. For more details, see the Hds::Interactive component.
Loading state
If the button needs to toggle between an "idle" and a "loading" state, we suggest applying a width to it (via inline style or CSS class) to prevent the button from resizing on click (and potentially causing layout shifts):
<Hds::Button
@icon=
@text=
/>
Disabled Buttons
To disable a Button, manually add the native disabled attribute:
<Hds::Button @text="Alert me" disabled />
Component API
size
enum
- small
- medium (default)
- large
color
enum
- primary (default)
- secondary
- tertiary
- critical
text
string
required
aria-label if isIconOnly is set to true. If no text value is defined an error will be thrown.
icon
string
Tertiary buttons have transparent backgrounds, and interactive elements must communicate interactivity with more than just color. Therefore, a leading or trailing icon is required when using the
tertiary color. WCAG 2.1 Criterion 1.4.1: Use of Color (Level A)
iconPosition
enum
- leading (default)
- trailing
isIconOnly
boolean
- false (default)
isFullWidth
boolean
- false (default)
isInline
boolean
- false (default)
@isInline parameter is provided, then the element will be displayed as inline-block (useful to achieve specific layouts). Otherwise, it will have a block layout.
href
<a> element.
isHrefExternal
boolean
- false (default)
<a> link is external and so for security reasons we need to add the target="_blank" and rel="noopener noreferrer" attributes to it.
route/models/model/query/current-when/replace
<LinkTo/LinkToExternal> component.
isRouteExternal
boolean
- false (default)
<LinkTo> is external to the Ember engine (more details here) in which case it will use a <LinkToExternal> instead of a simple <LinkTo> for the @route.
…attributes
...attributes.
Anatomy

| Element | Usage |
|---|---|
| Text* | Optional |
| Container | Required |
| Leading Icon* | Optional |
| Focus Ring | Focus state only |
| Trailing Icon* | Optional |
* One of these must be present.
States
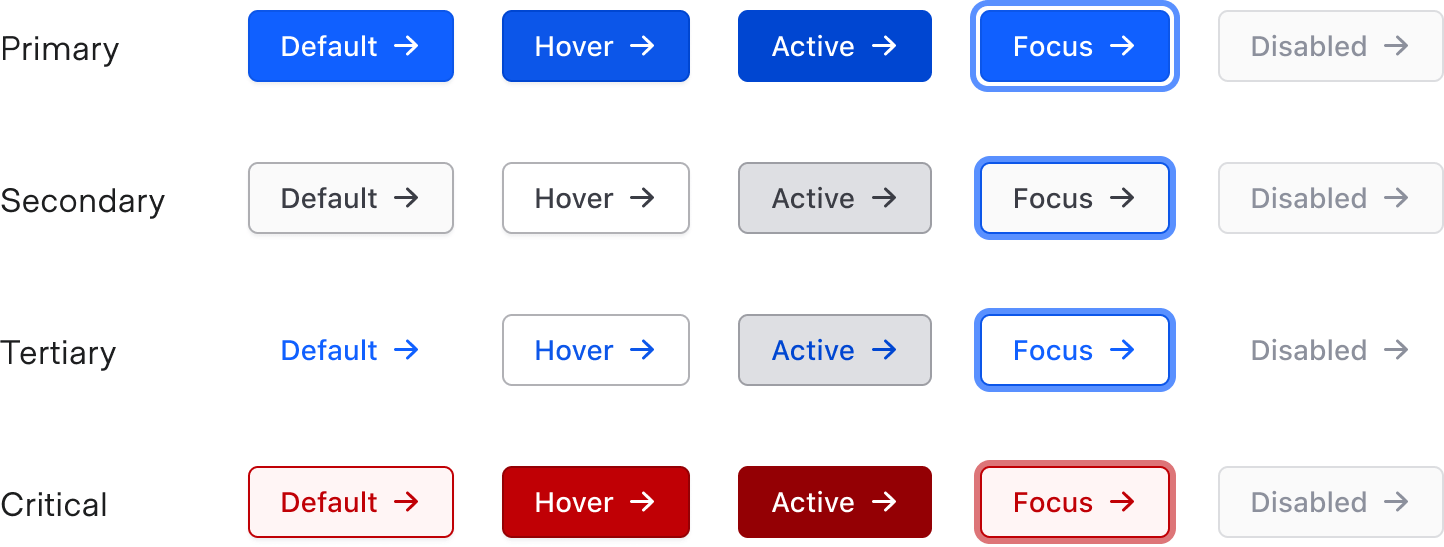
Disabled buttons should be used sparingly and with intention. Acceptable use cases for disabled buttons include:
- Incomplete flows (e.g., user has not yet completed a required action needed to move forward).
- Permissions restriction.
Conformance rating
When used as recommended, there should not be any WCAG conformance issues with this component.
Button vs. link
While buttons and links have been used interchangeably across the internet for years, understanding the difference between these two and striving for the semantic use of these elements can help make our products more conformant.
How to know which to use
- If it goes to a URL, use a Link.
- If it triggers an action (toggles a state, submits a form, etc.), use a Button.
- When submitting a form and redirecting the user to a different URL, use a Button.
Why strive for semantic use
Users with assistive technology (AT) or keyboard-only users rely on the semantic use of Buttons and Links to determine how to activate the element. Buttons are activated with the Enter/Return key or the Spacebar key, while Links can only be activated with the Enter/Return key.
Applicable WCAG Success Criteria
This section is for reference only. This component intends to conform to the following WCAG Success Criteria:
-
1.4.1
Use of Color (Level A):
Color is not used as the only visual means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element. -
1.4.10
Reflow (Level AA):
Content can be presented without loss of information or functionality, and without requiring scrolling in two dimensions. -
1.4.11
Non-text Contrast (Level AA):
The visual presentation of the following have a contrast ratio of at least 3:1 against adjacent color(s): user interface components; graphical objects. -
1.4.12
Text Spacing (Level AA):
No loss of content or functionality occurs by setting all of the following and by changing no other style property: line height set to 1.5; spacing following paragraphs set to at least 2x the font size; letter-spacing set at least 0.12x of the font size, word spacing set to at least 0.16 times the font size. -
1.4.3
Minimum Contrast (Level AA):
The visual presentation of text and images of text has a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 -
1.4.4
Resize Text (Level AA):
Except for captions and images of text, text can be resized without assistive technology up to 200 percent without loss of content or functionality. -
2.1.1
Keyboard (Level A):
All functionality of the content is operable through a keyboard interface. -
2.4.7
Focus Visible (Level AA):
Any keyboard operable user interface has a mode of operation where the keyboard focus indicator is visible. -
4.1.2
Name, Role, Value (Level A):
For all user interface components, the name and role can be programmatically determined; states, properties, and values that can be set by the user can be programmatically set; and notification of changes to these items is available to user agents, including assistive technologies.
Support
If any accessibility issues have been found within this component, let us know by submitting an issue.



